Articles

Mexican States
Southwest United States
Heritage and Governance
The Enemies of the Aztecs
“The Enemies of the Aztecs” will discuss the various groups who fought the Aztecs and were not conquered by them. In 1519, the Aztec Empire ruled over fifteen million people living in 489 communities in 38 provinces. Professor Michael E. Smith has stated that “one of the more intriguing characteristics of the Aztec Empire is the existence of major unconquered enemy states surrounded by imperial territory... Ethnohistoric sources from Tenochtitlán [the Aztec capital city] suggest that the Aztecs did not really want or need to conquer these states, and that they could easily have done so had they wished.” But Smith adds, “the boasts of the Mexica are better seen as propaganda than as accurate descriptions of political reality.” In fact, Smith’s research concluded that “the nature of the enemy states and their dealings with the empire shows that they were serious and powerful adversaries.”
Indigenous Veracruz and the Census
From 1895 to 2015, the Mexican census has painted a picture of Mexico’s people, providing details about languages spoken (Spanish, foreign and indigenous), religion, education, literacy, employment and migration. From the beginning, the Mexican census provided details about indigenous languages spoken by its citizens. However, in the first half century, it is possible that there were undercounts of indigenous language speakers because some may have failed to declare their language status for fear of affecting their position within the community. In addition, poor communications channels with rural, isolated indigenous communities may also have caused an undercount of the indigenous people.
The Africans of Mexico: From Slavery to the 2015 Census
Most people are not very aware of the presence of African slaves in colonial Mexico. In fact, some people believe that the influence of the African to Mexican culture is negligible at best. But the African laborer actually played an important and very indispensable role in the economic success of colonial Mexico. And, in some parts of Mexico, the African made cultural contributions.
The History of the Náhuatl Language: From Aztlán to the Present Day
The Uto-Aztecan Language Group includes a wide range of languages, stretching from Idaho and Montana all the way down to El Salvador in Central America. The Náhuatl language of the Aztecs represents only a small — but significant — part of this linguistic group.
The Náhuatl Language of Mexico: From Aztlán to the Present Day
Across the 761,606 square miles (1,972,550 square kilometers) that comprise Mexico you can find a great variety of landscapes and climates. While mountains and plateaus cover more than two-thirds of her landmass, the rest of Mexico’s environment is made up of deserts, tropical forests, and fertile valleys. Mexico’s many mountain ranges tend to split the country into countless smaller valleys, each forming a world of its own. Over the last few thousand years, this has been a factor in the differentiation of a wide range of indigenous Mexican languages.
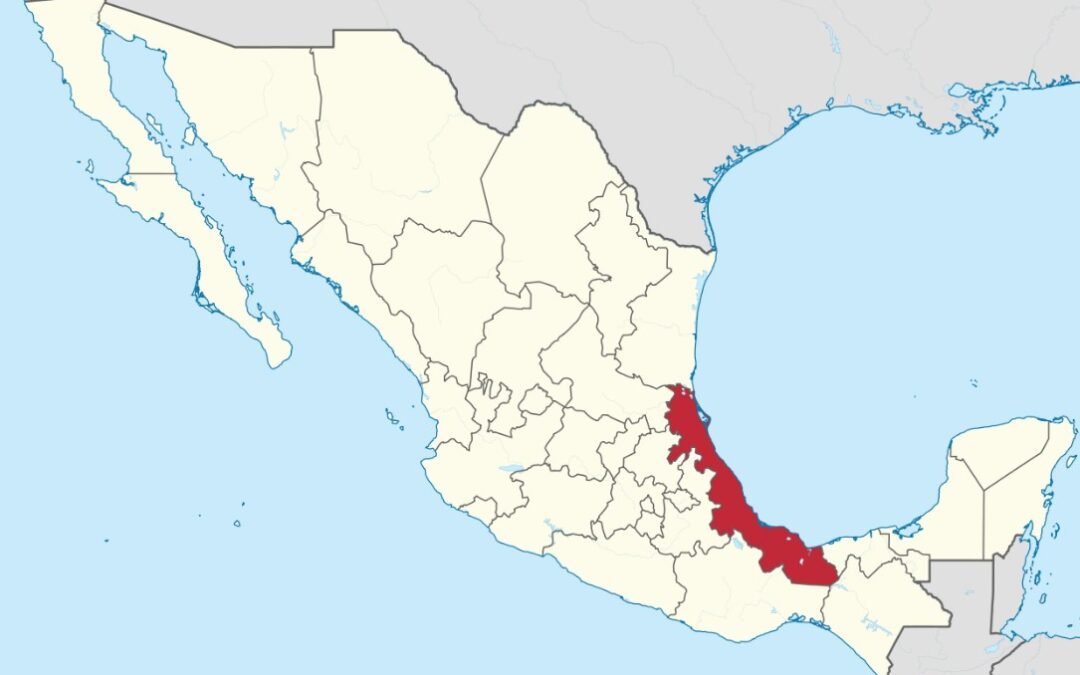
Veracruz: The Third Most Indigenous State of Mexico
The State of Veracruz, located along the eastern Gulf Coast of the Mexican Republic, shares common borders with the states of Tamaulipas (to the north), Oaxaca and Chiapas (to the south), Tabasco (to the southeast), and Puebla, Hidalgo, and San Luis Potosí (on the west). Veracruz also shares about 430 miles (690 kilometers) of its eastern boundary with the Gulf of Mexico.

Article Categories
- Aguascalientes 14
- Arizona 4
- Baja California 5
- Baja California Sur 2
- California 20
- Campeche 4
- Census 36
- Chiapas 3
- Chihuahua 11
- Coahuila 7
- Colima 1
- Conquistador Chronicles 2
- Durango 2
- Ethnic Identity 41
- Genealogy 35
- Guanajuato 8
- Guerrero 8
- Hidalgo 2
- Indigenous Insights 98
- Jalisco 25
- Mexico City 11
- Michoacan 7
- Morelos 4
- Nayarit 3
- New Mexico 4
- Nuevo Leon 7
- Oaxaca 6
- Politics 10
- Puebla 5
- Queretaro 1
- Quintana Roo 4
- San Luis Potosi 11
- Sinaloa 6
- Sonora 16
- Southwest US 26
- State of Mexico 5
- Tabasco 3
- Tamaulipas 11
- Texas 7
- Tlaxcala 7
- Veracruz 6
- Yucatan 6
- Zacatecas 13