Articles

Mexican States
Southwest United States
Heritage and Governance
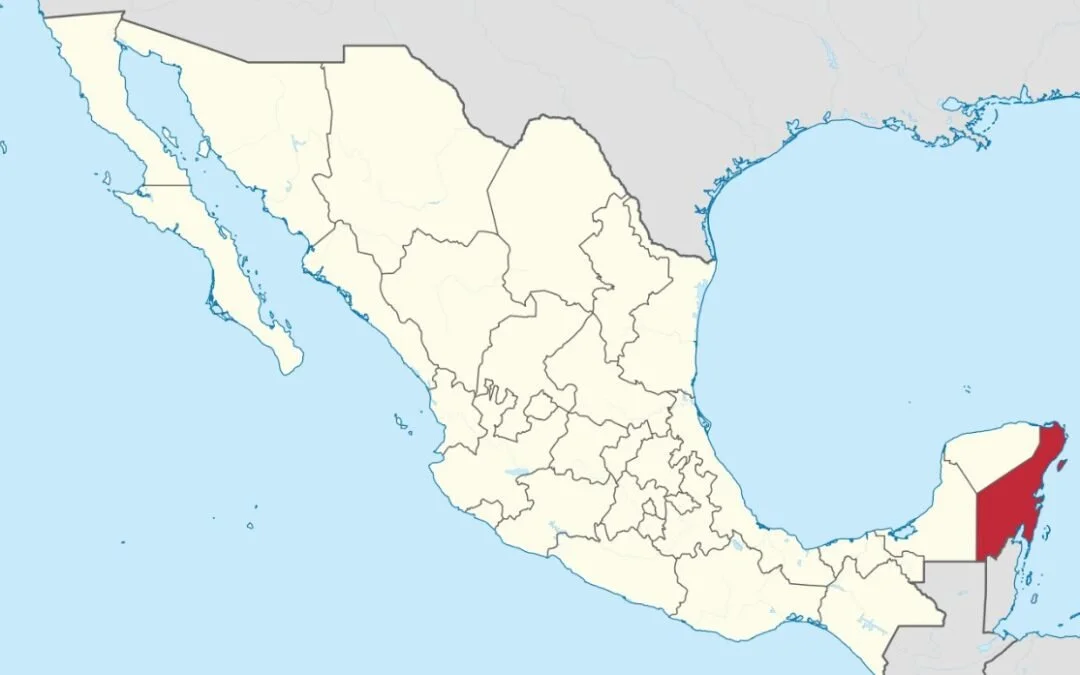
Quintana Roo and the Census
The present-day state of Quintana Roo is one of three Mexican states on the Yucatán Peninsula. In the pre-Hispanic period, Quintana Roo and the Yucatán were part of the Mayan World. In the colonial period, Quintana Roo became part of the Spanish Empire although much of the state maintained their Mayan culture and language.
Indigenous Jalisco and the Census
From 1895 to 2015, the Mexican census has painted a picture of Mexico’s people, providing details about languages spoken (Spanish, foreign and indigenous), religion, education, literacy, employment and migration. From the beginning, the Mexican census provided details about indigenous languages spoken by its citizens. However, in the first half century, it is possible that there were undercounts of indigenous language speakers because some may have failed to declare their language status for fear of affecting their position within the community. In addition, poor communications channels with rural, isolated indigenous communities may also have caused an undercount of the indigenous people.
Indigenous Michoacán and the Census
From 1895 to 2015, the Mexican census has painted a picture of Mexico´s people, providing details about languages spoken (Spanish, foreign and indigenous) religion, education, literacy, employment and migration. From the beginning, the Mexican census provided details about indigenous languages spoken by its citizens. However, in the first half century, it is possible that there were undercounts of indigenous language speakers because some may have failed to declare their language status for fear of affecting their position within the community. In addition, poor communications channels with rural, isolated indigenous, isolated indigenous communities may also have caused an undercount of indigenous people.
The Africans of Mexico: From Slavery to the 2015 Census
Most people are not very aware of the presence of African slaves in colonial Mexico. In fact, some people believe that the influence of the African to Mexican culture is negligible at best. But the African laborer actually played an important and very indispensable role in the economic success of colonial Mexico. And, in some parts of Mexico, the African made cultural contributions.
The Early Mexican Censuses (1793-1921)
Several estimates of the Mexican population in the late colonial period have been made. Present-day analysts suggest that the 1810 census was over estimated by nearly one-fifth. As noted below, roughly 60% of the population was indigenous in both 1793 and 1810. Persons identified as Spanish (white) who were born in Mexico – not Spain – represented nearly 18% of the population. Individuals of mixed origins (mestizos) represented one-fifth of the population.
Racial and Cultural Identity in Mexico: 2015
In 2016, the Mexican government agency, Instituto Nacional de Estadística Geografía e Informática (INEGI), published the 2015 Intercensal Survey, which upgraded Mexico’s socio-demographic information to the midpoint between the 2010 census and the census to be carried out in 2020. With a sample size of over 6 million homes, this survey provides information on the national, state and municipio level, as of March 15th, 2015.
Indigenous San Luis Potosí and the Census
From 1895 to 2015, the Mexican census has painted a picture of Mexico’s people, providing details about languages spoken (Spanish, foreign and indigenous), religion, education, literacy, employment and migration. From the beginning, the Mexican census provided details about indigenous languages spoken by its citizens. However, in the first half century, it is possible that there were undercounts of indigenous language speakers because some may have failed to declare their language status for fear of affecting their position within the community. In addition, poor communications channels with rural, isolated indigenous communities may also have caused an undercount of the indigenous people.
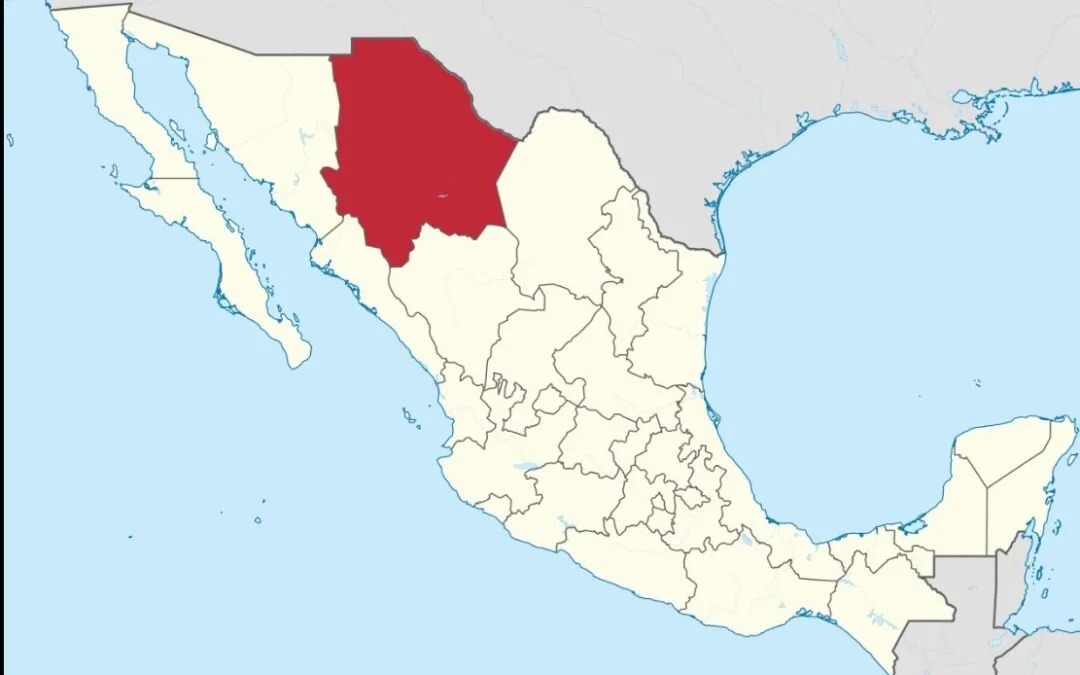
Indigenous Chihuahua and the Census
From 1895 to 2015, the Mexican census has painted a picture of Mexico’s people, providing details about languages spoken (Spanish, foreign and indigenous), religion, education, literacy, employment and migration. From the beginning, the Mexican census provided details about indigenous languages spoken by its citizens. However, in the first half century, it is possible that there were undercounts of indigenous language speakers because some may have failed to declare their language status for fear of affecting their position within the community. In addition, poor communications channels with rural, isolated indigenous communities may also have caused an undercount of the indigenous people.
Mexico’s 1921 Census: A Unique Perspective
In the aftermath of the Mexican revolution, Mexico’s Departamento de la Estadística Nacional administered a census that would be unique among Mexico’s census counts administered between 1895 and 2005. In this new census, the Mexican Government decided to ask Mexicans about their perception of their own racial heritage. In the 1921 census, residents of the Mexican Republic were asked if they fell into one of the following categories:
Indigenous Guerrero and the Census
The Mexican Census Paints a Picture
From 1895 to 2015, the Mexican census has painted a picture of Mexico’s people, providing details about languages spoken (Spanish, foreign and indigenous), religion, education, literacy, employment and migration. From the beginning, the Mexican census provided details about indigenous languages spoken by its citizens. However, in the first half century, it is possible that there were undercounts of indigenous language speakers because some may have failed to declare their language status for fear of affecting their position within the community. In addition, poor communications channels with rural, isolated indigenous communities may also have caused an undercount of the indigenous people.
Indigenous Nayarit and the Census
The State of Nayarit, located in northwestern Mexico, has an area of 27,857 square kilometers, thus taking up 1.4% of the national territory of Mexico and is the 23rd largest state. Nayarit’s 1,181,050 inhabitants occupy Nayarit’s twenty municipios but only ranks 29th among the 31 states and the Distrito Federal in terms of population. The capital of Nayarit is Tepic.
Mexico’s Indigenous Identity in the 2015 Intercensal Survey
In 2016, the Mexican government agency, Instituto Nacional de Estadística Geografía e Informática (INEGI), published the 2015 Intercensal Survey, which upgraded Mexico’s socio-demographic information to the midpoint between the 2010 census and the census to be carried out in 2020. With a sample size of over 6 million homes, this survey provides information on the national, state and municipio level, as of March 15th, 2015.
The Náhuatl Language of Mexico: From Aztlán to the Present Day
Across the 761,606 square miles (1,972,550 square kilometers) that comprise Mexico you can find a great variety of landscapes and climates. While mountains and plateaus cover more than two-thirds of her landmass, the rest of Mexico’s environment is made up of deserts, tropical forests, and fertile valleys. Mexico’s many mountain ranges tend to split the country into countless smaller valleys, each forming a world of its own. Over the last few thousand years, this has been a factor in the differentiation of a wide range of indigenous Mexican languages.
Speakers of Foreign Languages in Mexico (1910-1950)
It has been a well-established fact that the long-lived dictatorship of General Porfirio Díaz (1876 — 1911) ushered in an era of significant Mexican immigration. During the Porfiriato, the Mexican government sponsored the influx of foreign capital and immigrants as an essential ingredient to its nation building strategy.

Article Categories
- Aguascalientes 14
- Arizona 4
- Baja California 5
- Baja California Sur 3
- California 14
- Campeche 6
- Census 34
- Chiapas 4
- Chihuahua 14
- Coahuila 9
- Colima 1
- Conquistador Chronicles 2
- Durango 3
- Ethnic Identity 36
- Genealogy 32
- Guanajuato 9
- Guerrero 9
- Hidalgo 3
- Indigenous Insights 92
- Jalisco 25
- Mexico City 11
- Michoacan 7
- Morelos 5
- Nayarit 4
- New Mexico 3
- Nuevo Leon 8
- Oaxaca 6
- Politics 10
- Puebla 6
- Queretaro 2
- Quintana Roo 5
- San Luis Potosi 11
- Sinaloa 6
- Sonora 17
- Southwest US 23
- State of Mexico 6
- Tabasco 4
- Tamaulipas 12
- Texas 6
- Tlaxcala 7
- Veracruz 8
- Yucatan 6
- Zacatecas 13